⯈Algorithm and its Characteristics
⯈Elementary Problems
- Addition of two numbers
- Calculate area and circumference of circle
- Calculate area of triangle
- Calculate simple interest
- Calculate slope and distance between two points
- Convert length in feet to inches
- Weighted score in exam
- Convert temperature in degree Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Swap two numbers
- Swap two numbers without using extra variable
- Overview of C Programming Language
- Getting started with C Programming Language
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- Constants
- Operators
- Expression Evaluation
- Mathematical expression to C equivalent expressions
- Datatypes
- Variables
- Integer representation in C
- Character representation in C
- Type conversion in C
- sizeof operator
- Comments
- Mathematical Functions
- input output statements
- width specifiers in C
- structure of a C program
- header files
- Compilation process of a C program
- Types of initializations.
⯈Basic C Programs
- C program to add two numbers
- C program to find area and circumference of circle
- C program to swap two numbers
- C program to swap two numbers without using extra variable
- C program to swap two numbers using bitwise XOR
- C program to convert temperature in Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C program to calculate gross salary of an employee
- C program to count number of digits in a positive integer
- C program to count number of digits in binary representation
- C program to count number of digits in base ‘K’
- C program to convert kilometer to meter, feet, inches and centimeters
- C program to find first and last digit of a number
- C program to find minimum number of currency denominations
- C program to convert cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates
- C program to find distance between two places on earth in nautical miles
- C program to find slope and distance between two points
- C program to add 1 to the number using ‘+’ operator
- C program to find maximum of two numbers using ternary operator
- C program to find maximum of three numbers using ternary operator
- C program to find kth bit of a number
- C program to find last four bits of a byte
- C Program to reset right most set bit of a number
Compilation process of a C Program
Compilation is a process of converting high level programming to machine level language.
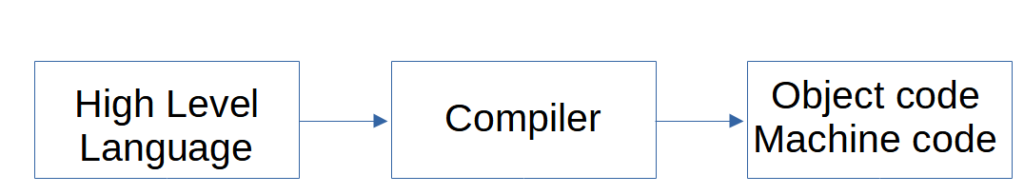
The compiler goes through the following steps to convert it to the machine code or object code.
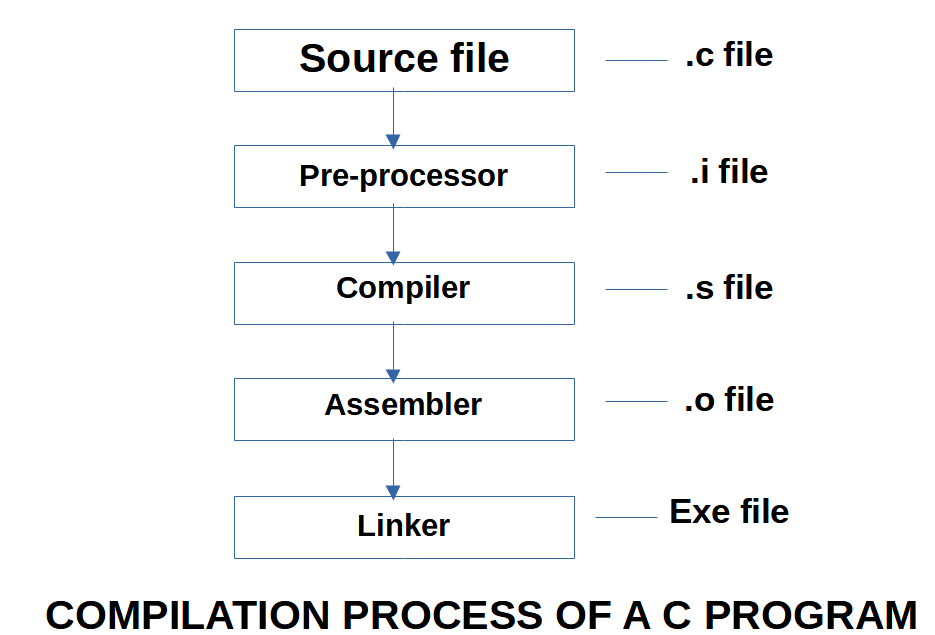
You may watch the video at the end of this page.
Source file
- The source file is written with the .c extension.
- This file is in high level language and cannot be understood by the machine, so needs to convert to low level language.
Pre-processor
- This is the first pass of the compiler.
- The pre-processor removes:
- comments.
- expansion of the included files.
- expands the MACROS or mainfest constants.
- conditional compilation.
- The pre-processor creates the .i file.
Compiling
- In this step the .i file is compiled to the .s file
- The .s file is created with the filename of test.s (since test is the C file that we have created)
Assembling
- In this step the .s file is converted to the .o (object file)
- The object file is the one which the machine understands, and we execute the object file.
Linker
The linker links all the function calls. If any function definition is missing or there is a mismatch, then the linker reports an error.
Writing C program and executing using gcc compiler on linux terminal
We write the program using the editor. Let us use the gedit editor.
gedit test.c
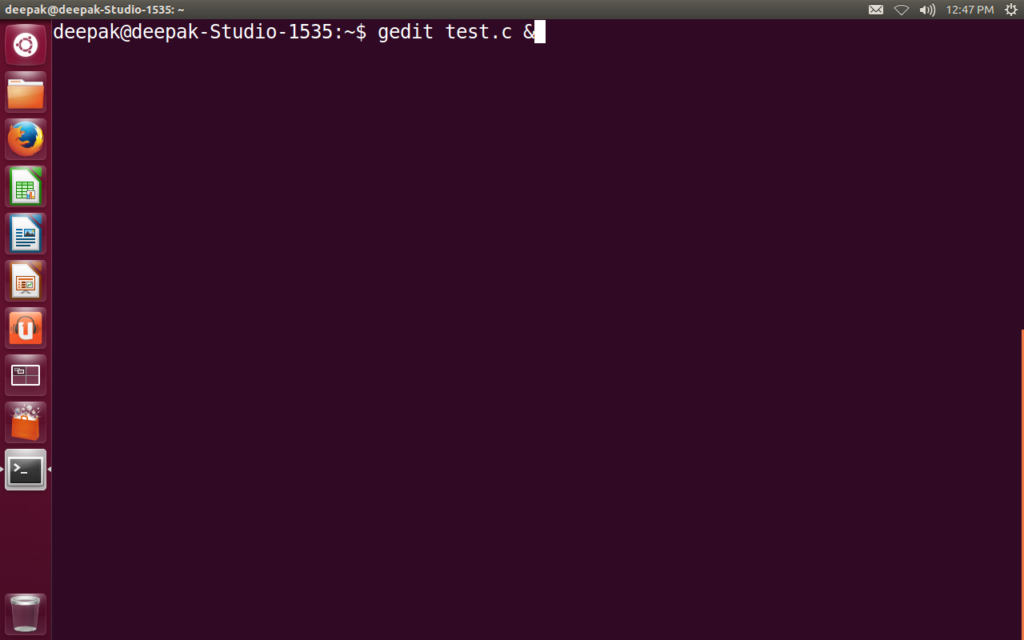
We write the program in the file,
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Welcome to geteducate.org\n");
return 0;
}
To convert this file (test.c) to machine language we use compiler, gcc and we compile file as,
gcc test.c
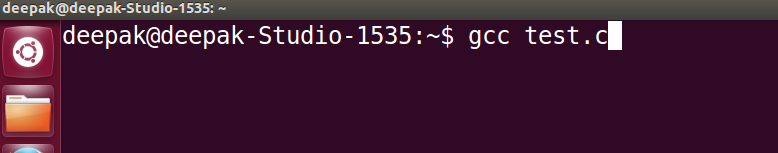
By default, it creates an object file with name a.out
To execute the object file we write,
./a.out
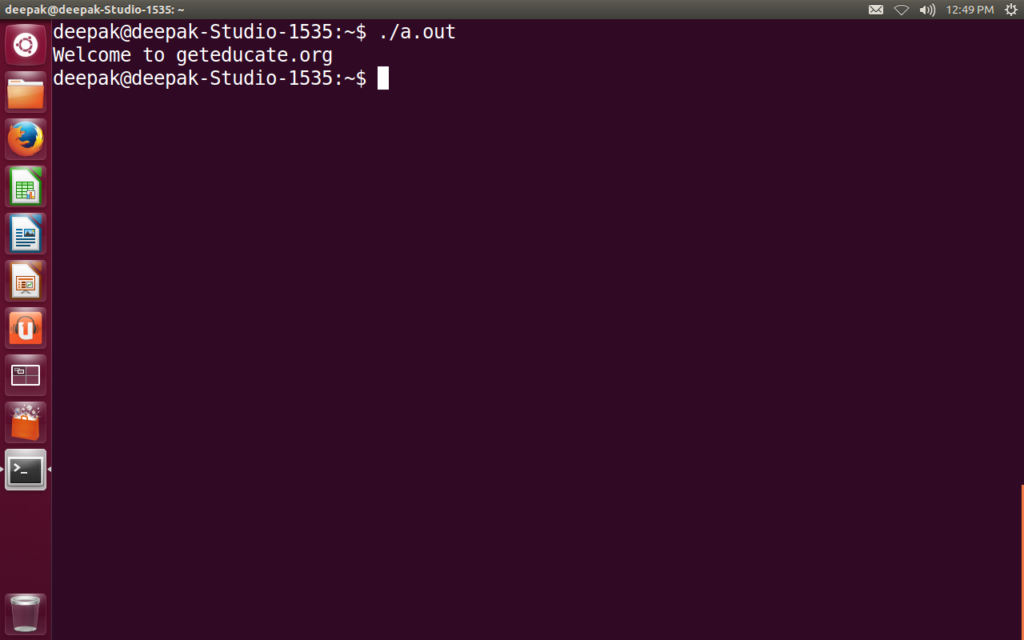
We can change the name of the object file using -o option of gcc.
gcc test.c -o test
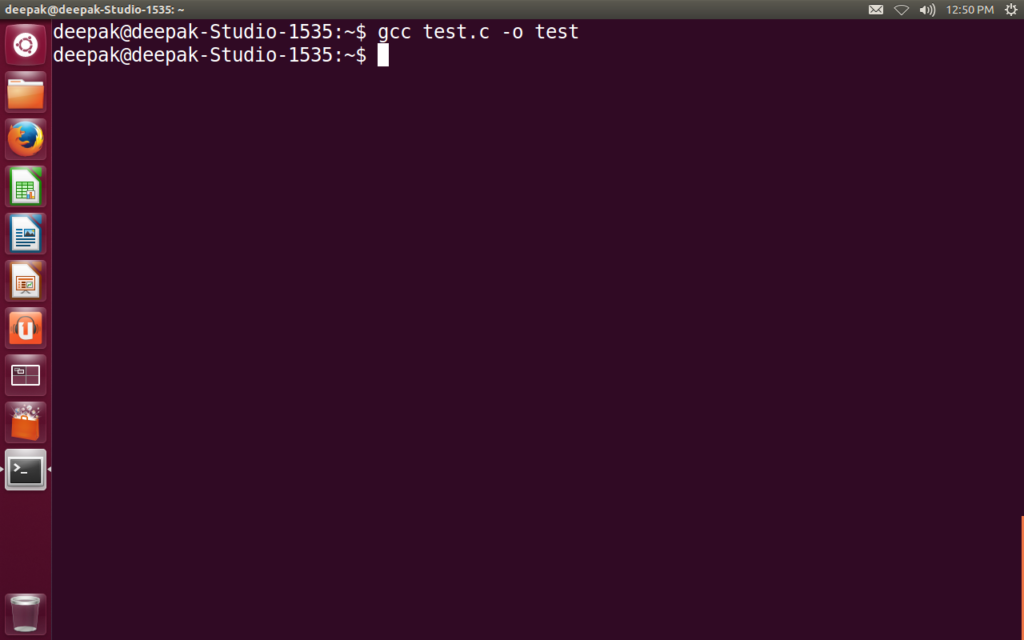
Creates an object file with name test instead of a.out
To execute,
./test
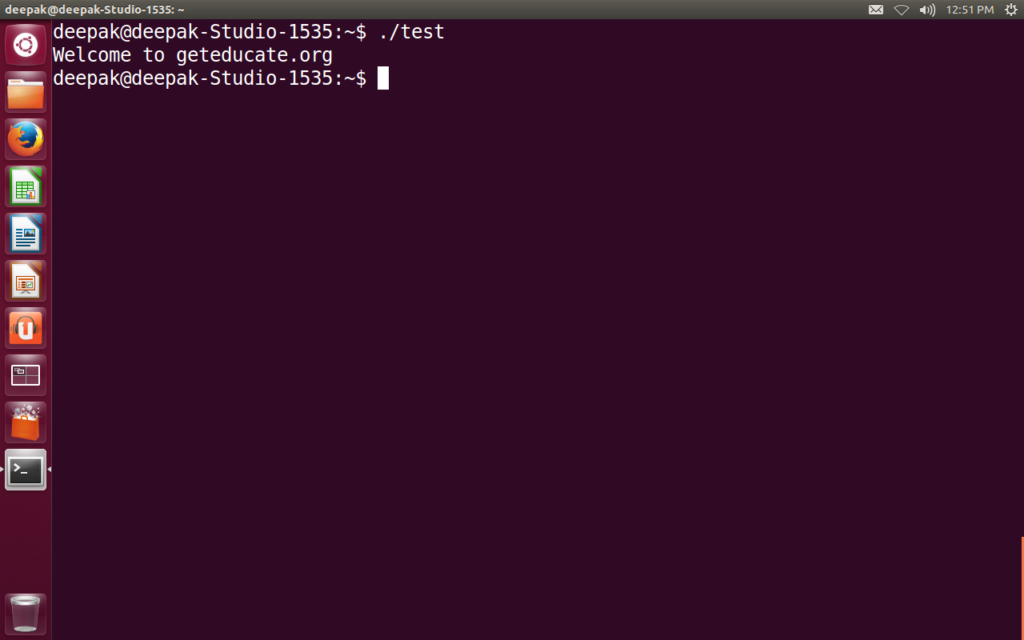
Note:
- We execute the .o file not the .c file
- Hence any modifications in .c file has to be recompiled to overwrite the .o file
